Nowadays, nearly everyone running a business online thinks about search engine optimization (SEO). There are countless blogs, videos, and even books that help to explain how to make your website better conditioned for this.
Without good SEO, your site might be hard to find. Even if your content is great, and even if you have the best enterprise network security products, you still need SEO.
One part of SEO that sometimes gets overlooked is the images. Of course, pictures are an essential part of any website for many different reasons – they break up walls of text, they can be interesting or attractive, they’re a way to add color and life to a page.
There are mountains of theory on how to create good images in terms of content and especially image design for marketing psychology. Here, though, we are going to look at how we can create good images in terms of search engine optimization.
SEO is an especially competitive field, which is why you should learn as much about it as you can. However, the great thing when teaching yourself is that everything you learn can be put into practice almost immediately.
That’s what we hope to provide here – some actionable tips that can optimize your website images for SEO. The tips below should be useful whether you’re a business intelligence analyst or a freelancer, so let’s get started.
Minimizing File Size
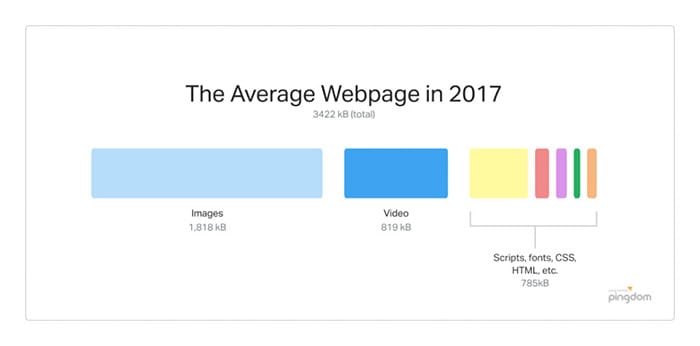
Images make up the bulk of the size of a website.
One key factor in search engine optimization is page load times. Google admits this, both for desktop and for mobile. The overall performance of a site improves its SEO ranking.
A mistake made by many sites is to ignore how large their images are, especially because they assume that most people are running on broadband or 4G. That’s a problem, because even though the site might load fast, others might load faster or have better performance generally.
You might find that a lack of communication between your image design team and developers has led to some large file sizes on images. Here are some things you can check.
#1. Choose the Right File Extension
There are generally three choices: GIF, JPG, and PNG. GIF only really has the advantage in absolute low file sizes, or as moving pictures, because the quality loss is noticeable.
As you can see on the images below, JPG and PNG have almost the same picture quality, but JPG is smaller. This makes JPG a superior choice for photographic images, but if you apply JPG to text, you can see what happens at the bottom of the image.


For images with typefaces, or infographics, use PNG. For photography, use JPG. Otherwise, your pretty typeface might end up looking like the example above.
A final point – do not mix text over photography or you will have to upload a photograph in PNG, which is inefficient for SEO purposes.
#2. Compress Images
Compression is really important to reducing the size of images that you host. Ideally, you want images to be under 100kb – if they’re too big, and you can’t cut the file size anymore, the best thing is to compress.
There are two excellent web services for compressing images. ImageOptim works best for JPG, and TinyPNG for PNG.
#3. File Dimensions
Make sure that the dimensions of your image are the same as the dimensions that it actually shows on the browser. For example, if the maximum width an image displays on a page is 640px, then your site will resize this image regardless of the overall dimensions.
This is fine if your image is 640px in width, but if it’s 9,600px, then your performance will suffer. Users will have to load a gigantic image only for it to be automatically resized anyway.
Go through your site and check the actual size of your images, then make sure they’re resized appropriately and reuploaded. You can work on SEO by making sure images are as small as they can be.
#4. Don’t Use Too Many Colors
More colors make a file much larger than it needs to be if those colors don’t really add anything to the image. This is true for photographs, illustrations, and infographics.
White space is especially effective at lowering load times and increasing performance, which is beneficial for SEO. Not every part of your website needs to be colored: you will notice in many modern websites there is a lot of blank white space.
The File
There are a lot of things you can do with the file itself and its place in your website.
#5. File Names
It’s critical for SEO that you name your images according to keywords, rather than random strings like IMG_1701. The more descriptive your file names, the better. The names should be easy to understand both for a search engine algorithm and a person.
For example, if you are writing a blog post about WFO workforce optimization, name screenshots something like workforce_optimization_pro.png, or something even more descriptive like software_for_workforce_optimization.png.
It might take a little bit of work to rename all your files, but you could do it tomorrow, and it would improve your SEO. The more, the better: even your customer communications icons should have SEO-friendly file names if possible.
#6. File Structure
According to the new Google guidelines, the file paths are now important for SEO rankings. This means that the directories in your website ought to be named appropriately for the images within.
Don’t just put all your images in an /images or /media folder. Make separate directories for each category. So for example, if you want to store images for a page on inbound contact center software, consider putting them all in a directory like /software.
Like renaming the files, it might be a bit of work if your website is large, but it will immediately help your SEO ranking.
#7 Alt Text
Google puts a high value on alt text relative to its actual function. Rather than just leaving alt text blank or putting generic phrases like “picture” or “icon”, try to actually describe what the image is for or what’s happening in it.
Google takes information from that alt text and generates clues from it. Smart – but that means your alt text of “picture1.jpg” gives the search engine absolutely no useful information whatsoever.
Notice that even the icons on this blog about cloud based call center software have alt text named for SEO. The alt text on the icon reads Mailshake Sales & Marketing Blog which is an excellent way to get more keywords into your ranking.
Once again – a couple of lines of code and you can improve your SEO.
Good examples of alt text:
#8. Image Files on the Sitemap
Your site should have a sitemap, a file where information about your site, including its contents, pages, videos and images, and so on are stored. Google reads your sitemap in order to process your site more accurately, so if you haven’t put your image files on your sitemap, you should straight away.
The sitemap allows Google to index your images more efficiently by analyzing the relationship between content on a website. It also allows Google to “see” images that they won’t find directly from your pages. That means that if your customer service pages are all run by a script, the images will still be visible to Google if they’re in a sitemap.
WordPress’s Yoast plugin does this automatically, but if you need to do it manually, Google has instructions.
#9. Browser Cache
Browser caching is a way to increase your site’s performance. When you load a page for the first time, your browser has to download all the images – but, if it saves them to the cache, the next time you load the page there’s no need to download again.
This is important for performance, so important for SEO. Google’s PageSpeed Insight will even show you if it thinks browser caching can help you.
Some hosts like WordPress can do caching automatically (otherwise you’ll have to write the code in yourself).
Images As Content
Just like video improves experience, so do images. Images are a fundamental part of your website.
The content has to engage people, have a purpose, and make the experience better. It doesn’t work to simply place images with keywords in the URL. Even alt text has to be helpful.
The original purpose of alt text is to help visually impaired people or people with slow internet to understand what an image is about. For example, this website addressing the question of what does IVR stand for has alt text describing exactly what the images show: “employee taking a call from a customer” for instance.
If your content is good, people will visit your site. If the images are good, people will source them or go to them from search engines. That’s the bottom line.
These actionable tips to optimize your images can make your SEO ranking better, but they can’t make a bad website good. That’s up to you.
Bio: Elea Andrea Almazora– RingCentral US
 Elea is the SEO Content Optimization manager for RingCentral, the leader in global enterprise communication, collaboration solutions on the cloud and fax software provider.. She has more than a decade’s worth of experience in on-page optimization, editorial production, and digital publishing. She spends her free time learning new things.
Elea is the SEO Content Optimization manager for RingCentral, the leader in global enterprise communication, collaboration solutions on the cloud and fax software provider.. She has more than a decade’s worth of experience in on-page optimization, editorial production, and digital publishing. She spends her free time learning new things.
Main Post Photo by Merakist on Unsplash



